
Product Excellence Through Modern PLM in Fast-Paced Markets
Modern PLM systems empower businesses to achieve product excellence in fast-paced markets by enhancing collaboration, agility and innovation.
In the daily operations of accountants and controllers, transactions involving G/L accounts or cost centers are commonplace. The accuracy of managing the master data for these entities is paramount. Often, this master data is handled through complex ticketing systems, email exchanges, or phone calls. Upon scrutinizing these processes, common justifications like “It’s always been done this way” or “It’s evolved over time” frequently emerge. Moreover, complex company structures often entail exceptions to standard procedures, necessitating extensive familiarization. MDM software, explained here using the example of SAP MDG Finance, standardizes processes, creates clear governance structures, and increases data quality.
SAP MDG Finance, also known as SAP Master Data Governance for Finance, is a solution from SAP that centrally manages financial master data within an organization. All new financial master data entries or modifications to existing ones are exclusively handled within SAP MDG-F, ensuring seamless synchronization across predefined target systems. This facilitates efficient collaboration across departments and systems. While SAP MDG-F can manage various master data objects, the implementation process typically prioritizes key entities such as G/L accounts and cost centers, depending on the organization’s needs, existing processes, budget, and system landscape.
The advantages of SAP MDG Finance solution are extensive:
In complex companies with several legal entities, numerous local master data processes can lead to significant discrepancies in data quality, balance sheet structures, and hierarchies across different regions. Nevertheless, maintaining close coordination with central accounting becomes indispensable, particularly during tasks like consolidating annual financial statements or using lean ledger approaches.
A fundamental aspect of SAP MDG Finance is its capacity to standardize processes. For example, central accounting can be directly involved from the outset of G/L account creation. The following illustration shows an example of a workflow as it might look in practice.
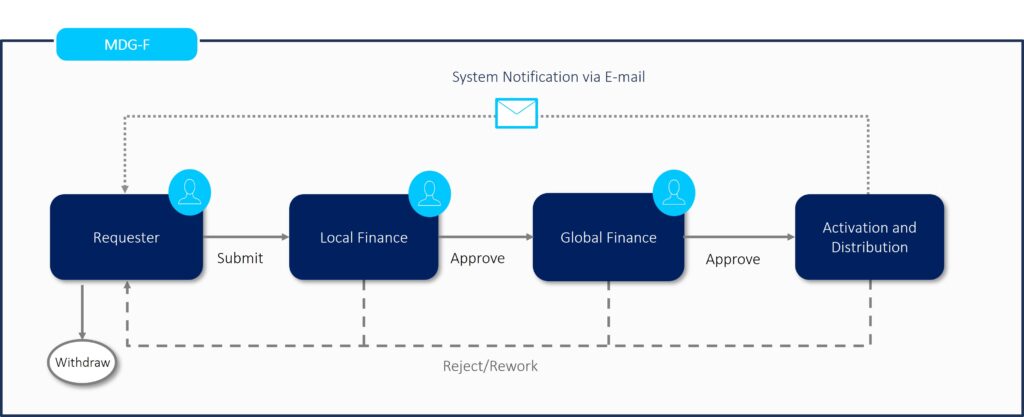
The introduction of standardized workflows presents companies with an opportunity to define clear responsibilities and role profiles for each step of the process. For instance, ensuring the authority of a central controlling team over the numbering logic of cost centers can be achieved by mandating that the creation of any new cost center receives approval from the central controlling department.
In this regard, it is often beneficial to consider establishing a centralized master data organization. While roles like data owners may not directly participate in workflows, they play a crucial role in establishing standards for various master data objects. These standards, in turn, are vital for end users who populate the individual master data fields within the workflows. Camelot has successfully promoted the establishment of central master data organizations in a large number of projects. Read more about Camelot’s data governance approach here.
Several factors contribute to increased master data quality.
One of the most important aspects is the dual control principle. During the approval of a change request, at least one person must approve the change, depending on the process design. In this way, one or more control instances can be installed.
Another aspect to consider is the implementation of business rules, which encompass various types.
SAP MDG Finance empowers you to establish transparent and uniform master data processes while assigning responsibilities effectively. Coupled with robust governance, this enables you to establish internal standards for your master data, leading to a lasting enhancement in data quality. Consequently, your internal and external financial reporting stands to benefit significantly.
Should you identify opportunities for improvement within your company’s master data processes, governance structures, or data quality, consider the adoption of a central master data organization alongside the SAP MDG Finance solution. Camelot provides solutions that enable precise governance distribution and seamless SAP MDG-F implementation.

Modern PLM systems empower businesses to achieve product excellence in fast-paced markets by enhancing collaboration, agility and innovation.

Read how the Campaign Planner & Designer (CPD) helps you to manage supply chain variability.

Explore automated production planning with our Campaign Planner & Designer.

The pharma market trends impact logistics with a shift to smaller, higher-value shipments and new temperature requirements.
© Camelot Management Consultants, Part of Accenture