
AI-Driven Application & Process Testing: Embracing Agentic Testing
Learn how Agentic AI enables digital transformation, delivering true hyperautomation.

In today’s digital age, finance departments constantly have to navigate the complex landscape of data management. As the digital transformation accelerates, the emphasis often shifts to elaborate strategies and advanced tools. However, beneath these sophisticated processes and tools, there is a plain truth: even the most advanced strategies in the world fail without a stable foundation. In finance, this stability and reliability is rooted in the financial master data. Amid the bustling conversations about agility and optimization, it’s crucial to remember that the foundation of successful finance operations is the integrity and accuracy of its foundational data.
For enterprises operating within an SAP ecosystem, the most recommended tool to ensure flawless financial master data management is SAP MDG-Finance (MDG-F). While SAP MDG caters to various master data domains, such as business partner data and material master data, it is the MDG-F module that stands out for financial data management, covering areas like controlling, accounting, treasury, and consolidation.
The need for high-quality financial master data becomes even clearer when we delve into the very essence of financial processes:
As companies consider a S/4HANA implementation, the importance of a robust master data framework becomes increasingly critical. In the area of data migration, especially in a transformative move to S/4HANA, confidence in flawless financial master data is essential. Without a solid foundation, the entire migration process runs the risk of getting bogged down in data inconsistencies and long delays. SAP MDG-F proves to be a decisive factor in this context. Not only does it ensure the highest quality of financial master data, but it also eliminates the need for tedious manual data entry or complex mass upload functions into various systems. With MDG-F, companies can avoid potential pitfalls in financial data migration and ensure a fast and smooth transition to S/4HANA.
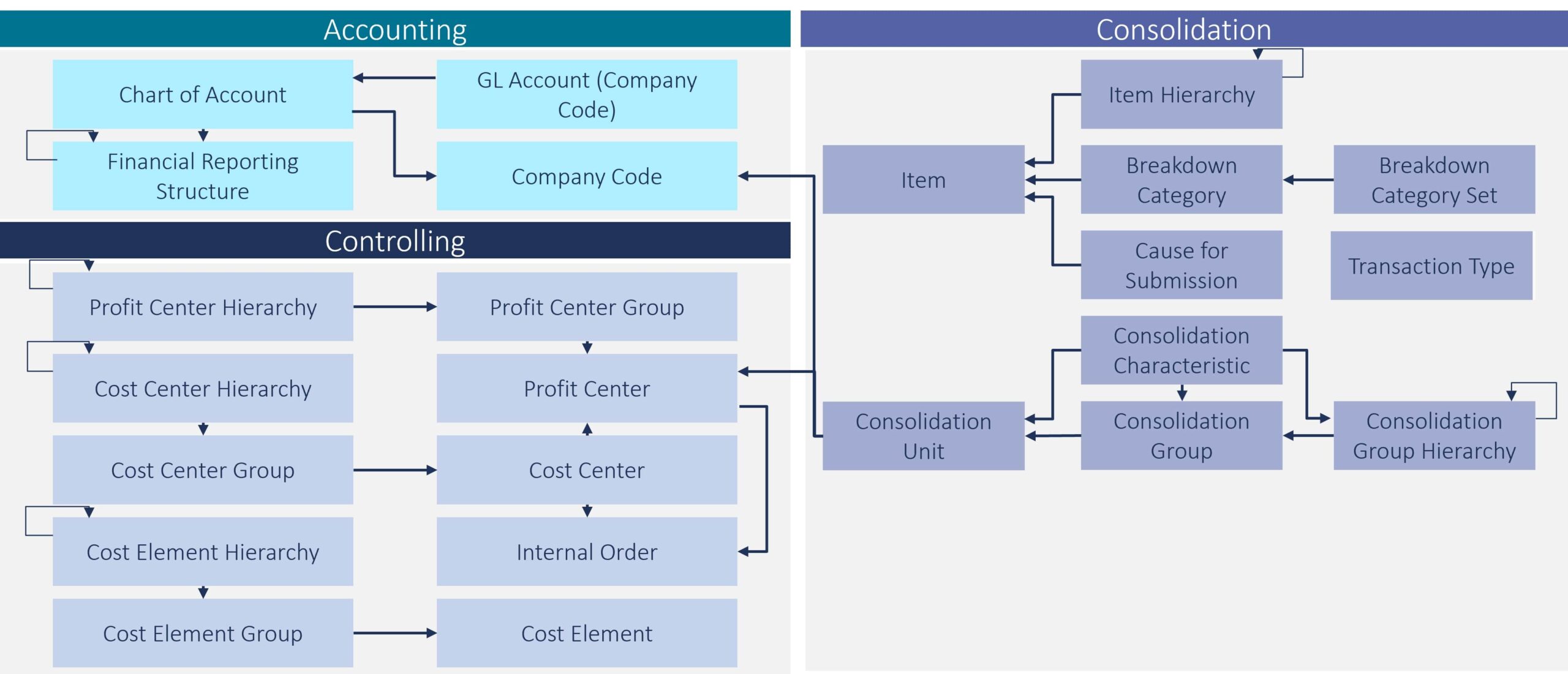
The data model of MDG-F is meticulously structured into three clusters to address the diverse nuances of financial data:
In addition to these clusters, organizations can further extend the data model to incorporate other master data aspects like bank master data.
The beauty of SAP MDG-F lies in its granular role-based approach to data governance. By defining specific roles within an organization, businesses can ensure that each step in the master data process is managed by individuals or teams with the appropriate expertise and responsibilities.
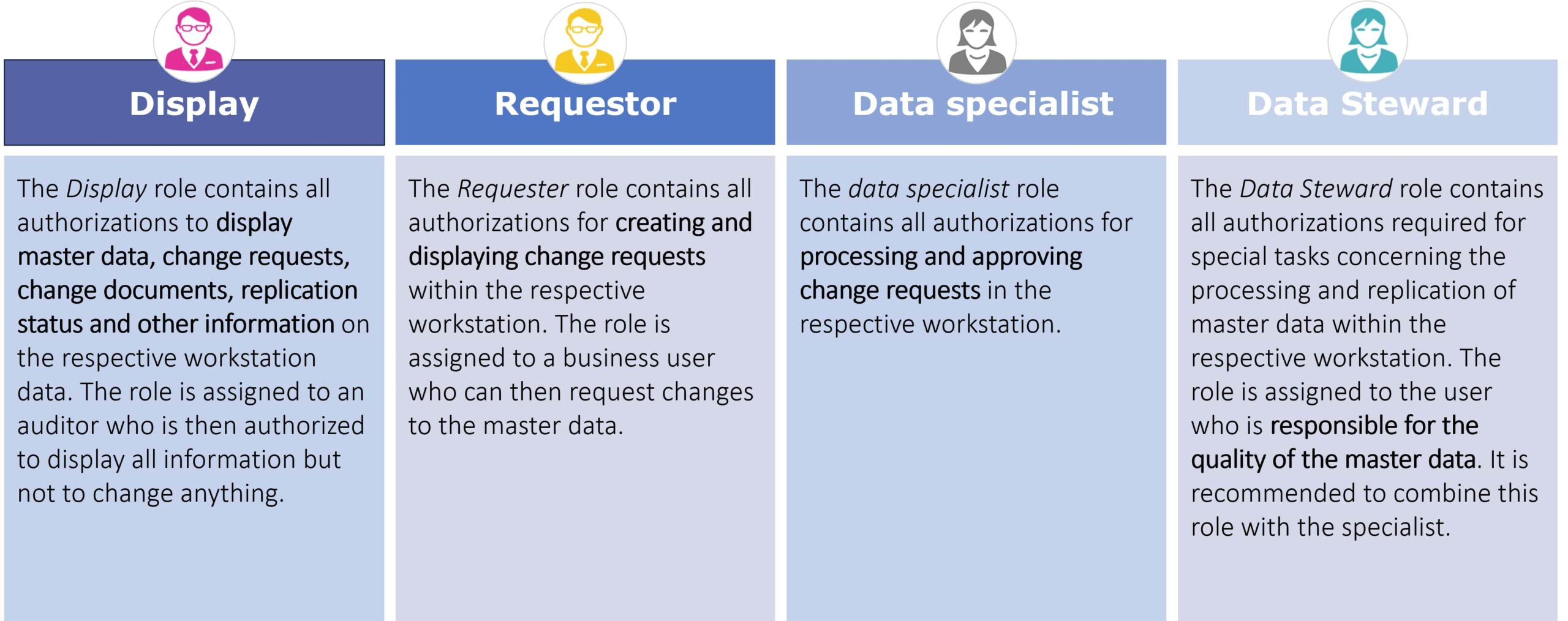
These roles aren’t just nominal. They are assigned to specific steps in the data governance process, ensuring clarity, accountability, and precision. The role-based approach not only provides a clear path of data governance, but also ensures that any modifications or alterations are monitored, checked, and validated by the appropriate stakeholders. This minimizes errors, ensures compliance, and accelerates the process of data management.
Diving deeper into the data management process, MDG-F introduces robust workflow capabilities. For each data object, predefined workflows are established for actions such as Create, Change, Block, and Mark for Deletion. These workflows outline the essential steps needed for each of these activities.
The depth of these workflows can range from a simple single-stage process to intricate five-stage workflows, contingent on the organization’s complexity and the governance requirements associated with each data object modification. By default, MDG-F comes with a two-tiered workflow (See figure 3 for a visual representation of the process involved in creating a cost center in MDG-F).
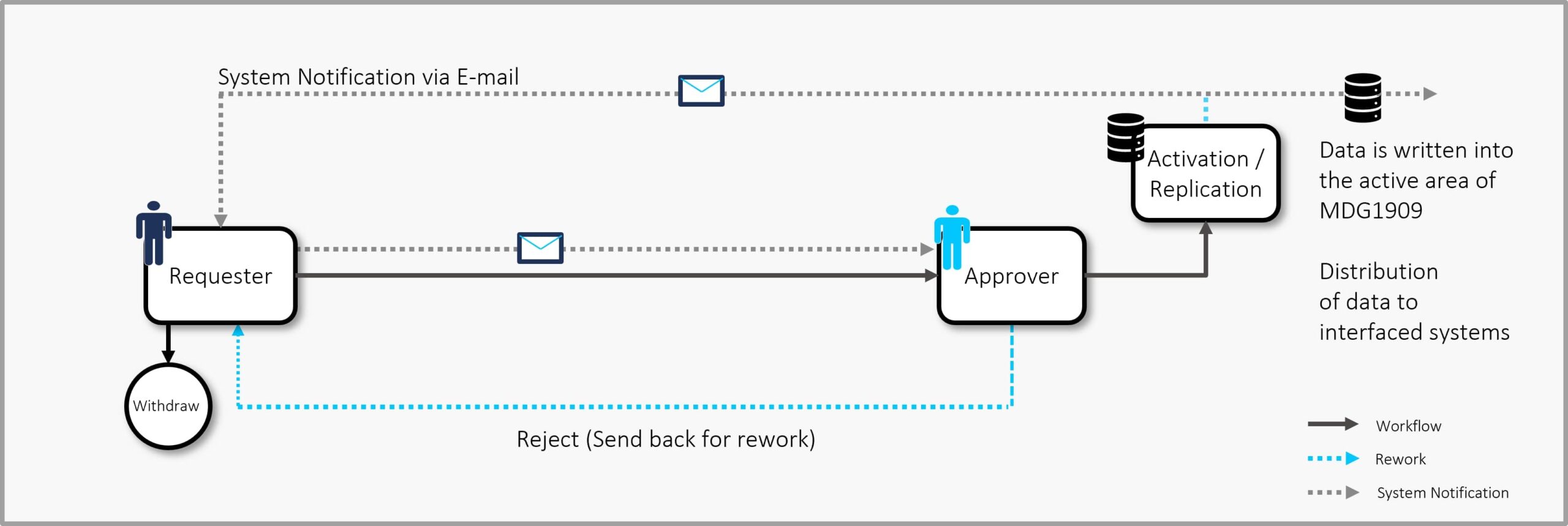
Each process invariably kicks off with the initiation of a Change Request. This request captures the specific modifications (be it Create, Change, Block, or Mark for Deletion) intended for the data object. As the workflow progresses, various roles (as defined in the role-based governance model) come into play, ensuring that each step is thoroughly vetted and validated. The workflow concludes with the pivotal approval step, followed by the replication of the master data through the staging area to the connected systems.
Combining role-based governance with structured workflows, SAP MDG-F offers businesses a holistic, efficient, and error-minimized approach to financial master data management. With clearly defined roles attending to their specific steps in the workflow, businesses can be confident about the quality and accuracy of their data. The strategic integration of these two components underscores the tool’s utility, reinforcing the idea that with the right systems in place, master data management doesn’t have to be a tedious task, but rather a streamlined, accountable, and efficient process.
In the tangled corridors of finance, time dependencies are not only common but often crucial. When it comes to situations that demand anticipation, such as an upcoming merger or a major reshaping of the existing master data structure, SAP MDG-F’s ‘Edition’ model stands out as a very valuable tool.
An edition serves as more than just a container; it’s a forward-looking strategy tool, enveloping all change requests set to become active at a predetermined future time. Thus, an edition becomes an embodiment of planned changes.
In scenarios like an anticipated merger, the Edition model allows businesses to pre-configure their financial master data structures comprehensively. This means the complete blueprint of how the master data landscape would look post-merger can be set up well in advance. Likewise, for extensive changes or adaptations to the existing master data landscape, the entire change can be holistically prepared within an edition.
One of the standout features of the Edition model is its flexibility in determining activation dates. Companies can set a specific ‘Valid-From Date’, ensuring that the changes within an edition become active precisely when needed. This precision not only guarantees synchronization across the master data but also ensures that the data is replicated seamlessly to all connected systems from that specified date.
This predictive approach, facilitated by editions, drastically reduces the operational disruptions usually associated with major financial restructuring events. Thus, the Edition model in MDG-F is not just a feature but a strategic advantage, ensuring organizations are always a step ahead in their financial master data governance.
As businesses accelerate their journey towards digital transformation and undertake initiatives like the S/4HANA migration and numerous micro-process optimizations, it’s paramount not to sideline the core – the master data. Embracing solutions like SAP MDG-F isn’t just a step towards modernization; it’s an essential pivot for today’s finance departments targeting precision, compliance, and unparalleled excellence. In the vast orchestration of business processes, the adage rings truer than ever: “Well begun is half done.” Securing a rigorous master data governance with SAP MDG-F marks a promising start.
We would like to thank Johannes Hopf for his valuable contribution to this article.

Learn how Agentic AI enables digital transformation, delivering true hyperautomation.

Reimagine resilience and proactively minimize supply chain risks

This article shall help you to understand how to optimize your inventory positions in a month – or even less.

Modern PLM systems empower businesses to achieve product excellence in fast-paced markets by enhancing collaboration, agility and innovation.
© Camelot Management Consultants, Part of Accenture
Camelot Management Consultants is the brand name through which the member firms Camelot Management Consultants GmbH, Camelot ITLab GmbH and their local subsidiaries operate and deliver their services.